Air pollution emerges as one of the leading causes of environmental health problems globally today. Addressing this critical issue, both the European Union (EU) and the United States (US), as major global economies, have taken significant steps towards updating air quality standards to improve public health and environmental sustainability.

Updates on Air Quality Standards by the EU
Despite advancements in air quality over the past three decades, the EU acknowledges that air pollution remains a significant challenge to environmental health, prompting significant measures to reduce environmental health risks. On February 20, 2024, representatives from the EU Council and the European Parliament reached a provisional political agreement on proposing new EU air quality standards to achieve zero pollution and contribute to a non-toxic environment.
The new rules aim to establish stricter EU air quality standards for 2030, which will be more in line with World Health Organization (WHO) guidelines and regularly reviewed threshold and target values.
The revised directive covers a range of air pollutants such as fine particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), sulfur dioxide (SO2), benzo(a)pyrene, arsenic, lead, and nickel. Special standards are set for each pollutant, with annual limit values for pollutants like PM2.5 and NO2, which significantly affect human health, being halved.
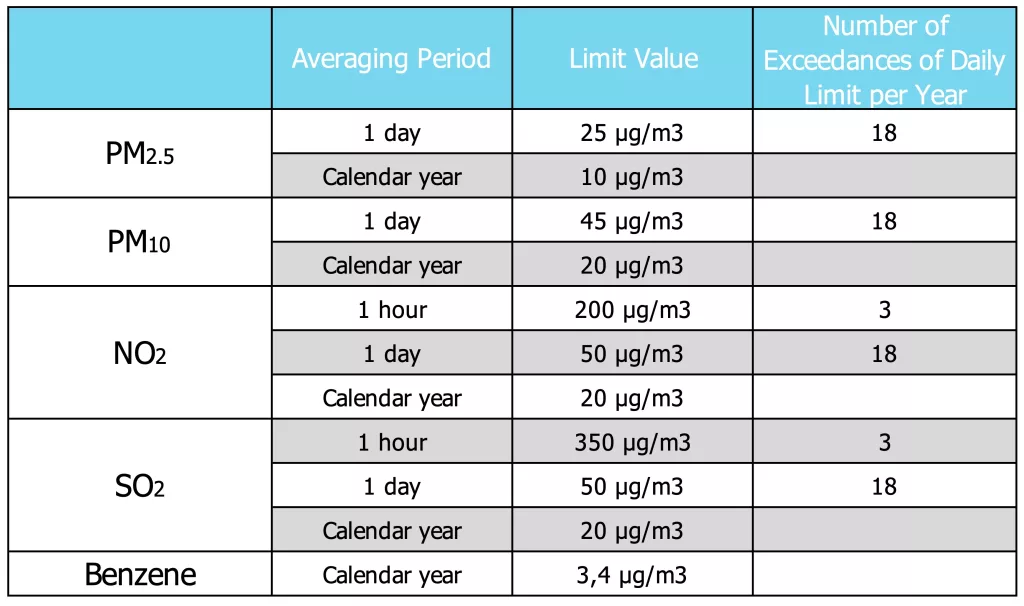
Furthermore, the new rules also require member states to develop roadmaps and air quality plans if levels of specific pollutants exceed the defined threshold or target values. Additionally, short-term action plans must be established to mitigate emergency risks when warning thresholds are exceeded.
Updates on Air Quality Standards by the US
On February 7, 2024, the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) updated the National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS) for Particulate Matter and the Air Quality Index to protect millions of Americans from heart attacks, premature death, and other health issues. This update was a significant step towards a cleaner environment by reducing the annual PM2.5 standards from 12.0 micrograms per cubic meter to 9.0 micrograms per cubic meter.
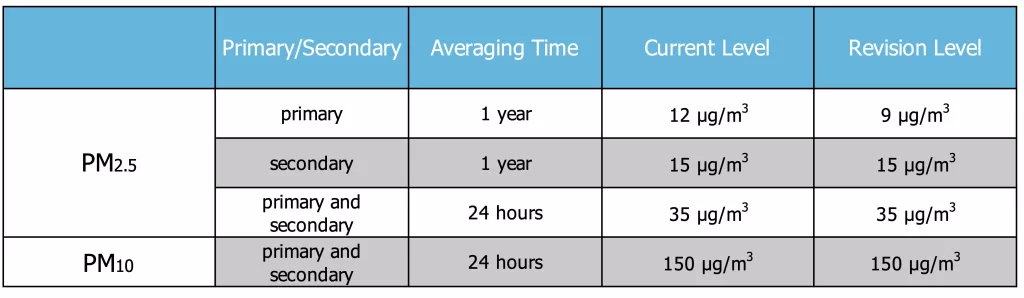
The EPA’s new standards address long-standing concerns raised by public health experts and environmental activists. PM2.5 pollution can lead to serious health problems such as respiratory diseases, cardiovascular issues, and cancer, posing a significant risk, especially to vulnerable communities. These new standards aim to provide a healthier future, particularly for at-risk groups like children, the elderly, and individuals with health conditions. However, primary and secondary 24-hour PM2.5 standards, secondary PM2.5 standards, and primary and secondary PM10 standards remain unchanged without revision.

Alongside this significant move by the EPA, improvements are being made in communication and monitoring aspects such as updates to the Air Quality Index and changes in the monitoring network. This will enable the public to gain more information about air quality and enhance protective measures in communities exposed to excessive pollution. The new HKI breakpoints will also be used on the AirNow website after being published in the Federal Register for 60 days.
The decision of the EPA reflects a science-backed approach, and it is expected that these changes will have a positive impact on public health. According to the EPA’s estimates, with the implementation of these new standards, it will be possible to prevent 4,500 premature deaths and avoid 290,000 lost workdays. Additionally, it is anticipated that there will be a net health benefit of $46 billion by 2032.
Since 2000, there has been a 42% decrease in PM2.5 concentrations in outdoor air, while the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of the United States has increased by 52% during the same period. These data demonstrate that efforts to improve environmental quality have not harmed economic growth; on the contrary, they have enhanced health and well-being.
EPA Administrator Michael S. Regan emphasizes that these new standards will protect the most vulnerable and overburdened communities in the US, contributing to overall national health improvement. He states that this step will help people lead healthier and more productive lives, ultimately increasing the nation’s health and well-being in the long run.
The update of air quality standards by both the EU and the US signifies a significant commitment and step towards environmental and public health. These updates could potentially improve the quality of life for millions by providing cleaner air and a healthier environment. As stated by Abigail Dillen, President of Earthjustice, such federal standards are crucial for protecting public health and ensuring environmental justice.
The alignment of air quality limit values and regulations in Türkiye with the updated standards of the EU and the US is of utmost importance. While the existence of a draft regulation is a positive step, clarity on details is necessary during the process of publication and implementation of this regulation. Additionally, some values specified in the current draft regulation fall short of the updated limit values of the EU and the US and the thresholds set by the WHO. This underscores the necessity for Türkiye to align its commitments and efforts regarding air quality with similar efforts by the EU and the US. This alignment is vital for complying with international standards and contributing more effectively to global environmental conservation efforts.
References
Council of the EU. (2024). Air quality: Council and Parliament strike deal to strengthen standards in the EU.
EPA. (2024). Final Updates to the Air Quality Index (AQI) for Particulate Matter Fact Sheet and Common Questions.
See The Air. (2024). The European Union Agreed on New Rules & PM2.5/NO2 Limits for Cleaner Air.









