Temperature warnings were issued one after another across the Turkiye and the world, while the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) announced El Niño. The WMO announced that El Niño is currently underway and there is a 90 percent chance that it will continue at a medium or higher strength by the end of the year. Temperature records are already being broken, and El Niño could push the world beyond a new average temperature record.
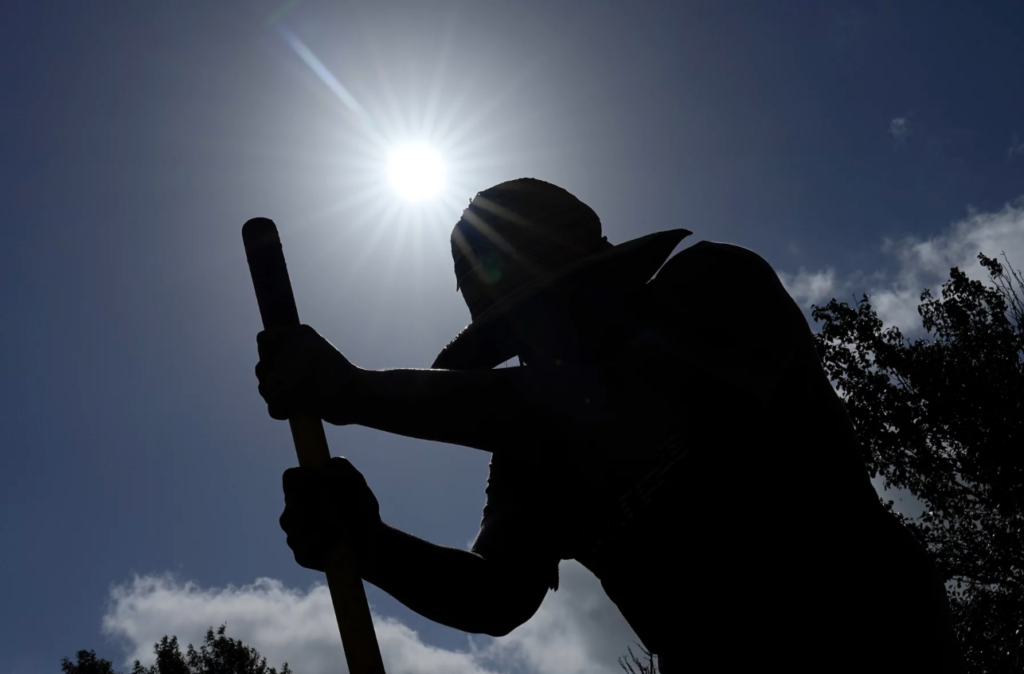

What is an El Niño event?
Under normal conditions, the surface water in the Pacific Ocean is colder in the east and warmer in the west. “Tayrial winds” tend to blow from east to west, and heat from the sun gradually warms the waters as they move in that direction. During El Niño events, these winds weaken or reverse and instead send warm surface waters eastward. This means that warmer water spreads more and stays closer to the surface. This releases more heat into the atmosphere, creating more humid and warmer air.
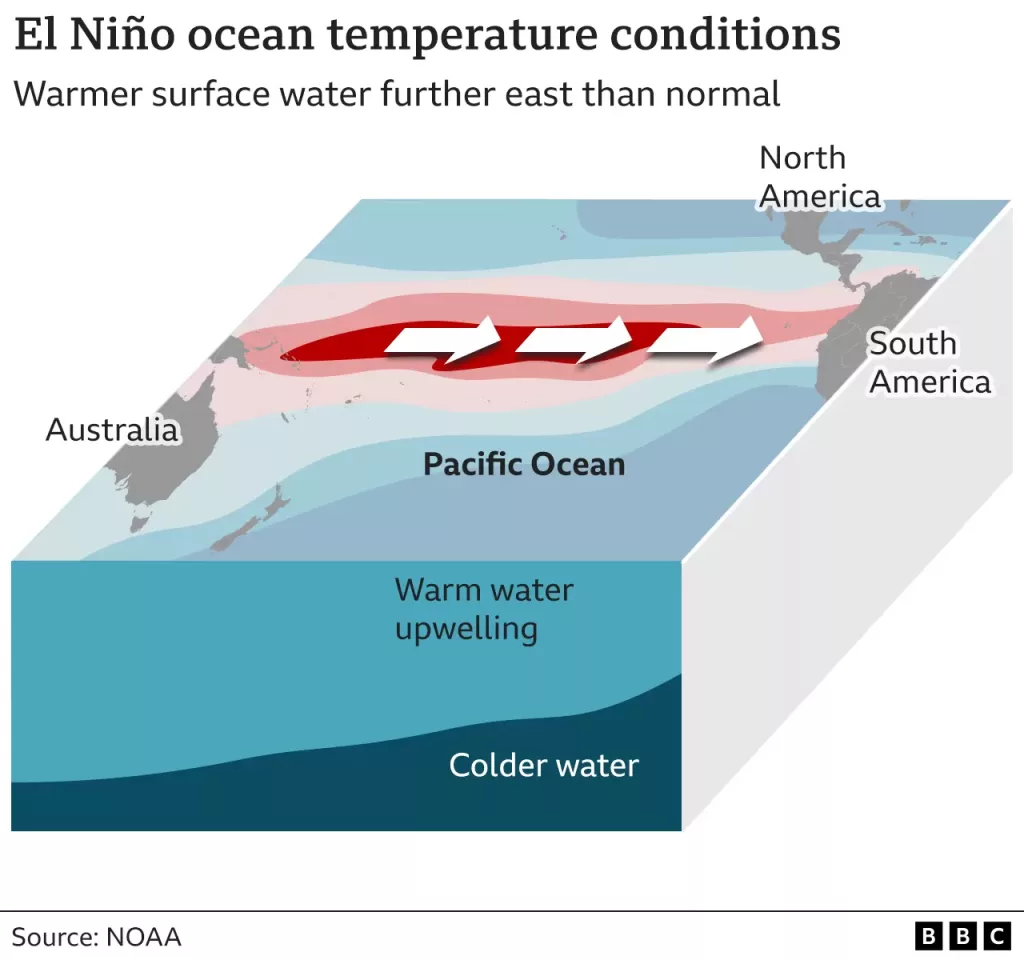
An El Niño event is typically declared when sea surface temperatures in the tropical eastern Pacific rise to at least 0.5 °C above the long-term average. The effects of this event are felt globally. This phenomenon affects pressure and temperature differences in the atmosphere, alters air currents, and leads to changes in precipitation patterns. As a result, the climatic conditions in different regions are affected. For example, normally arid regions may receive more rainfall, while normally rainy regions may experience drought.
Effects of El Niño
El Niño occurs on average every two to seven years and typically lasts nine to 12 months. The WMO says the first El Niño in seven years is coming. Seven years ago, the latest such event contributed to the drought and food insecurity that affected tens of millions of people in southern and eastern Africa. Climate change caused by humans burning fossil fuels and releasing greenhouse gases into the atmosphere is exacerbating the effects of the natural climate model.
Prof. Adam Scaife, head of long-term forecasting at the UK Met Office, said: “It is very likely that the next major El Niño will take us above 1.5°C. “The probability of spending the first year at 1.5°C in the next five-year period is currently about 50:50.”
The effects of this event not only cause changes in climate but can also have effects on human health. Excessively high temperatures make it impossible to work or exercise safely outside, exacerbate heart and lung disease, and worsen air pollution. Heat is especially dangerous for people working outdoors, infants, and the elderly. And when heat is combined with moisture, it is even more deadly. The impact of this event on global temperatures is usually seen the year after it occurs, so the impact of the latest event will likely be clear in 2024.
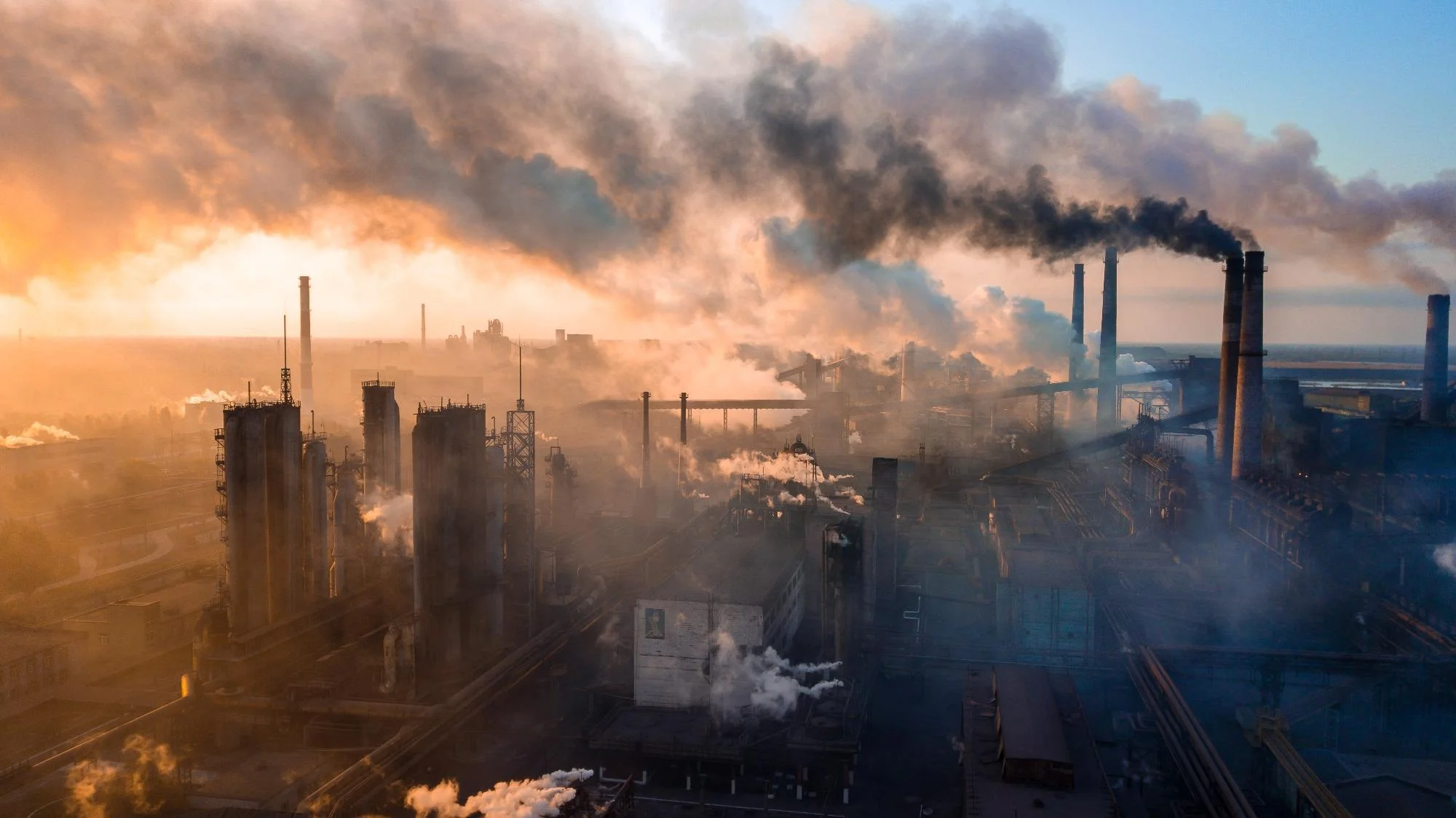
Effect of El Niño on air pollution
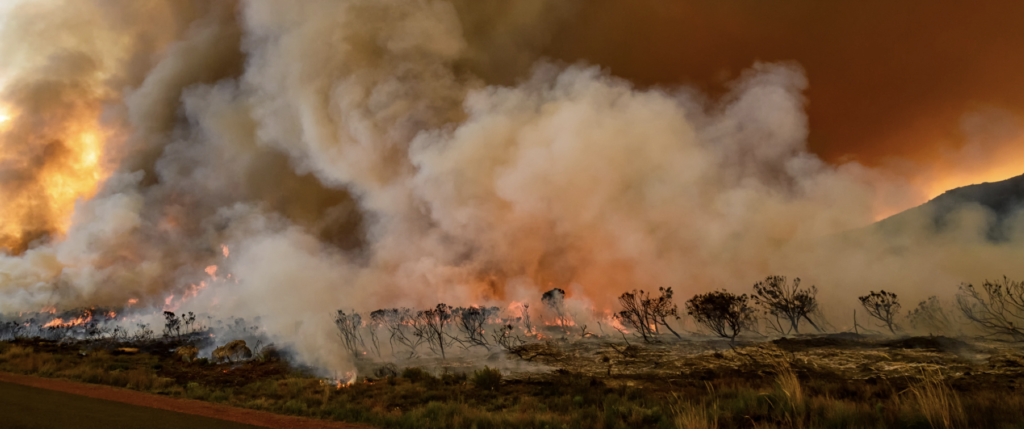

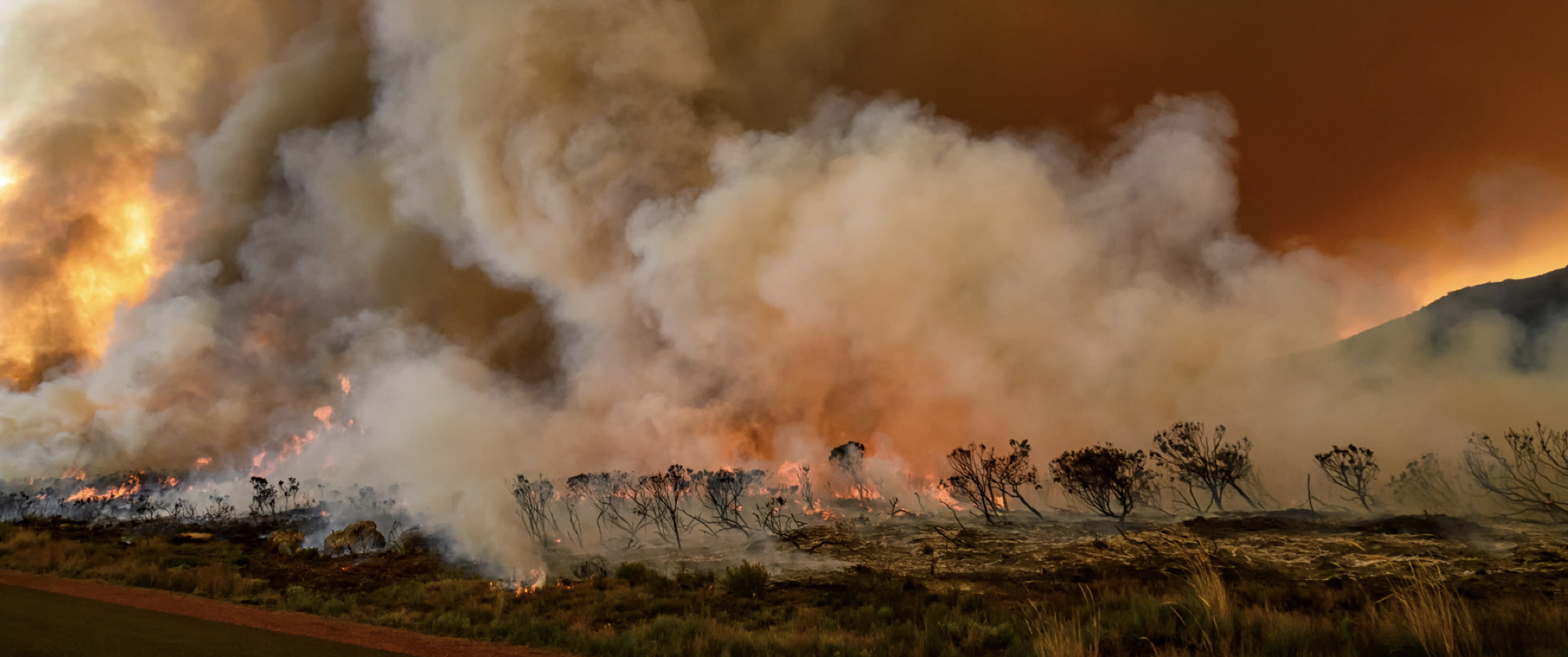
El Niño-related drought conditions can increase the risk of wildfires, which cause local and cross-border smoke pollution. Inhalation of fire smoke is a major public health problem that causes respiratory diseases and other harmful effects. The El Niño-related drought in 1997 contributed to the worsening of wildfires in Brazil, Indonesia, and Malaysia. In 2015, air quality in six Southeast Asian countries was affected by wildfires exacerbated by El Niño-related drought, including Indonesia, which declared a state of emergency due to dangerous air quality.
Another effect of this event is that it affects the distribution of pollutants in the atmosphere. In warmer and drier regions, the concentration of dust and particulate matter may increase. In addition, increased rainfall can cause natural disasters such as floods and floods, which can lead to the mixing of sources of pollution into water supplies and increased environmental pollution.
As a result, this event can cause climate change and many different effects around the world. With the breaking of temperature records, the effects of this event may become more evident and lead to significant changes in climatic conditions. Therefore, the importance of intervention and adaptation policies to climate change is increasing.









